دوره 19، شماره 3 - ( پاییز 1397 )
دوره، شماره، فصل و سال، شماره مسلسل |
برگشت به فهرست نسخه ها
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Esmailpour Nosar M, Hosseini S A, Akbarfahimi N, Tabatabai Ghomshe S F. Effect of Different Intensities of Harsh Reliance of Auditory Stimulation on Static Balance in 5-12 Years Old Children With Cerebral Palsy in Tehran City, Iran. jrehab 2018; 19 (3) :194-205
URL: http://rehabilitationj.uswr.ac.ir/article-1-2273-fa.html
URL: http://rehabilitationj.uswr.ac.ir/article-1-2273-fa.html
اسماعیل پور نوسر معصومه، حسینی سید علی، اکبر فهیمی نازیلا، طباطبایی قمشه سید فرهاد، بیگلریان اکبر. بررسی تأثیر تحریک شنیداری ناملایم با شدت متفاوت بر تعادل ایستای کودکان فلج مغزی اسپاستیک 5 تا 12 ساله در تهران. مجله توانبخشی. 1397; 19 (3) :194-205
URL: http://rehabilitationj.uswr.ac.ir/article-1-2273-fa.html
معصومه اسماعیل پور نوسر1 

 ، سید علی حسینی1
، سید علی حسینی1 

 ، نازیلا اکبر فهیمی*2
، نازیلا اکبر فهیمی*2 

 ، سید فرهاد طباطبایی قمشه3
، سید فرهاد طباطبایی قمشه3 

 ، اکبر بیگلریان4
، اکبر بیگلریان4 


 ، سید علی حسینی1
، سید علی حسینی1 

 ، نازیلا اکبر فهیمی*2
، نازیلا اکبر فهیمی*2 

 ، سید فرهاد طباطبایی قمشه3
، سید فرهاد طباطبایی قمشه3 

 ، اکبر بیگلریان4
، اکبر بیگلریان4 
1- گروه کاردرمانی، دانشگاه علوم بهزیستی و توانبخشی، تهران، ایران.
2- گروه کاردرمانی، دانشگاه علوم بهزیستی و توانبخشی، تهران، ایران. ،na.akbarfahimi@uswr.ac.ir
3- گروه ارگونومی، دانشگاه علوم بهزیستی و توانبخشی، تهران، ایران.
4- گروه آمار زیستی، دانشگاه علوم بهزیستی و توانبخشی، تهران، ایران.
2- گروه کاردرمانی، دانشگاه علوم بهزیستی و توانبخشی، تهران، ایران. ،
3- گروه ارگونومی، دانشگاه علوم بهزیستی و توانبخشی، تهران، ایران.
4- گروه آمار زیستی، دانشگاه علوم بهزیستی و توانبخشی، تهران، ایران.
متن کامل [PDF 685 kb]
(2383 دریافت)
| چکیده (HTML) (6433 مشاهده)
References
متن کامل: (2582 مشاهده)
مقدمه
فلج مغزی اختلال حرکتی و وضعیتی ناشی از صدمه غیر پیشرونده در مغز در حال رشد است که از ضایعه مغزی پیش از تولد، حین تولد یا پس از تولد ناشی میشود [1]. شیوع آن در آمریکا 2 تا 2/5 مورد در هر هزار تولد زنده گزارش شده است [2, 3]. محل ضایعه بر رشد و کیفیت الگوهای حرکتی موجود در کودک مبتلا به فلج مغزی تأثیرگذار است [3]، به طوری که فلج مغزی نوع اسپاستیک نشاندهنده آسیب در قشر حرکتی است. ضایعات هستههای قاعدهای به طور معمول، نوسانات تون عضلانی به صورت دیستونی و اتتوز را به دنبال خواهد داشت. آسیب مخچه منجر به ایجاد عدم هماهنگی حرکتی میشود که مشخصه اصلی کودکان فلج مغزی نوع آتاکسیک است [3]. اسپاستیسیتی به طور تقریبی در 80 درصد از افراد فلج مغزی با تغییراتی بر تون عضلانی، قدرت، سفتی و رشد نمایان میشود [4]. اختلال در کنترل حرکتی و وضعیت به عنوان شایعترین اختلال حرکتی در این کودکان است [5 ،3].
کنترل وضعیت فرایندهای پیچیده و مداومی است که به تنظیم موقعیت بدن در فضا به منظور ثبات و جهتیابی اطلاق میشود که طی فرایند یکپارچهسازی نیروهای درونی و بیرونی و عوامل محیطی انجام میگیرد [6]. ثبات وضعیتی یا تعادل ایستا به معنی توانایی حفظ مرکز توده بدن در محدوده تعادل است. این محدوده، بخشی از فضاست که بدن میتواند وضعیتش را در آن بدون تغییر در سطح اتکا، حفظ کند. بنابراین مرز ثابتی ندارد و حدود آن بستگی به نوع فعالیت، بیومکانیک فرد و جنبههای مختلف محیطی دارد [7]. هیچ ساختار منفردی بهتنهایی تعادل ایستا را تحت پوشش قرار نمیدهد، بلکه کنترل تعادل ایستا نتیجه اثر متقابل سیستمهای عضلانی، اسکلتی و عصبی است [7].
یکی از اجزای سیستم عصبی در کنترل تعادل ایستا، سیستمهای حسی است که برای درک موقعیت بدن در فضا باید اطلاعات دریافتی از گیرندههای حسی سیستمهای بینایی، سوماتوسنسوری (گیرندههای پوستی، مفاصل و عضلات)، وستیبولار و شنوایی را پردازش و سازماندهی کند. هر یک از این سیستمها به عنوان یک مرجع اطلاعاتی ویژه، اطلاعات خاصی را از وضعیت بدن در اختیار سیستم اعصاب مرکزی قرار میدهند [7].
سیستم سوماتوسنسوری اطلاعات مربوط به وضعیت بدن نسبت به سطح اتکا و ارتباط اجزای مختلف بدن نسبت به همدیگر را برای سیستم اعصاب مرکزی فراهم میکند. سیستم بینایی اطلاعات مربوط به وضعیت و حرکت سر را نسبت به اشیای موجود در محیط گزارش میدهد. اطلاعات سیستم وستیبولار منبع مهمی برای درک وضعیت و حرکت سر در ارتباط با نیروی جاذبه است [8]. گیرندههای شنوایی مسئول آگاهسازی فرد از ماهیت حرکات در محیط هستند [9 ،6]؛ به طوری که پاسخ بیش از حد به محرکهای شنیداری ممکن است به تغییر تون عضلانی منتهی شود که اغلب در کنترل حالت بدن و هماهنگی پاسخهای حرکتی مؤثر است [10 ،6]. این محرکات میتوانند به صورت قابل پیشبینی و غیر قابل پیشبینی ظاهر شوند و سبب فعال شدن سیستم دستگاه عصبی خودکار و بروز اختلال در حفظ تعادل ایستا شوند [11 ،6]. این اختلال میتواند به دو صورت حرکتی و شناختی بر عملکرد تعادلی فرد مؤثر باشد، تأثیرات حرکتی با افزایش تون عضلانی و بروز رفلکسهایی نظیر استارتل و مورو و تأثیرات شناختی با دشواری در توجه وتمرکز مشخص میشود [13-11].
کودکان فلج مغزی اسپاستیک تجربه کمی در رد (فیلتریشن) محرکات نامربوط دارند. توجه کارکردی آنها حین انجام تکالیف حرکتی با بیشترین محدودیت همراه است و نیاز به توجه اختصاصی برای انجام عملکردهای شناختی حین کنترل تعادل ایستا دارند [11]. در محیطهای پرمحرک مشکلات تعادل ایستا در کودکان فلج مغزی افزایش مییابد. از آنجایی که حفظ تعادل به تأثیر و کارآمدی پیشخوراندهایی از دروندادهای حسی متنوع وابسته است، اهمیت دروندادهای شنیداری از این لحاظ هنوز کاملاً مشخص نشده است [13 ،11].
با وجود آنکه اختلال درکنترل تعادل ایستا یکی از مشخصههای اصلی فلج مغزی و به عنوان عامل اصلی اختلال در کارکرد این کودکان مطرح است، مطالعات محدودی درباره روشهای بهبود کنترل تعادل ایستا در این کودکان صورت گرفته است [15 ،14]. برنامههای درمانی بیشتر در حوزههای اسبدرمانی [17 ،16]، آبدرمانی [18]، تکالیف دوگانه [20 ،19]، تردمیل [22 ،21] و چند برنامه تقویتی بود [24 ،23]. در بیشتر مطالعات تکالیف دوگانه به بررسی تداخل برنامههای شناختی [20] یا برنامههایی با تأکید بر حافظه کاری بینایی و کنترل تعادل ایستا پرداخته شده است [19].
با توجه به علائم گسترده در این کودکان، ضرورت اجرای مداخلات درمانی متعدد، تحقیقات محدود در حوزه تأثیر تحریکات شنیداری در تعادل کودکان فلج مغزی، و نقصان نتایج قطعی پیرامون ارتباط بین تعادل ایستا و تحریکات شنیداری، لزوم اجرای این پژوهش ضروری به نظر رسید. هدف از اجرای پژوهش، بررسی تأثیر تحریک شنیداری ناملایم با شدت متفاوت و سطح اتکا بر تعادل ایستای کودکان فلج مغزی اسپاستیک5 تا 12 ساله است.
روش بررسی
این تحقیق از نوع توصیفی تحلیلی بود که روی 20 کودک اسپاستیک 5 تا 12 سال شهر تهران انجام شد. برای محاسبه حجم نمونه، مقدار انحراف معیار در مطالعهای مشابه بررسی شد. حجم نمونه با استفاده از انحراف معیار با فرمول زیر محاسبه شد. در این فرمول انحراف معیار 0/15، z (ضریب اطمینان 95 درصد) 2/8، دقت احتمالی مطلوب d] 0/1 ]در نظر گرفته شده است.
فلج مغزی اختلال حرکتی و وضعیتی ناشی از صدمه غیر پیشرونده در مغز در حال رشد است که از ضایعه مغزی پیش از تولد، حین تولد یا پس از تولد ناشی میشود [1]. شیوع آن در آمریکا 2 تا 2/5 مورد در هر هزار تولد زنده گزارش شده است [2, 3]. محل ضایعه بر رشد و کیفیت الگوهای حرکتی موجود در کودک مبتلا به فلج مغزی تأثیرگذار است [3]، به طوری که فلج مغزی نوع اسپاستیک نشاندهنده آسیب در قشر حرکتی است. ضایعات هستههای قاعدهای به طور معمول، نوسانات تون عضلانی به صورت دیستونی و اتتوز را به دنبال خواهد داشت. آسیب مخچه منجر به ایجاد عدم هماهنگی حرکتی میشود که مشخصه اصلی کودکان فلج مغزی نوع آتاکسیک است [3]. اسپاستیسیتی به طور تقریبی در 80 درصد از افراد فلج مغزی با تغییراتی بر تون عضلانی، قدرت، سفتی و رشد نمایان میشود [4]. اختلال در کنترل حرکتی و وضعیت به عنوان شایعترین اختلال حرکتی در این کودکان است [5 ،3].
کنترل وضعیت فرایندهای پیچیده و مداومی است که به تنظیم موقعیت بدن در فضا به منظور ثبات و جهتیابی اطلاق میشود که طی فرایند یکپارچهسازی نیروهای درونی و بیرونی و عوامل محیطی انجام میگیرد [6]. ثبات وضعیتی یا تعادل ایستا به معنی توانایی حفظ مرکز توده بدن در محدوده تعادل است. این محدوده، بخشی از فضاست که بدن میتواند وضعیتش را در آن بدون تغییر در سطح اتکا، حفظ کند. بنابراین مرز ثابتی ندارد و حدود آن بستگی به نوع فعالیت، بیومکانیک فرد و جنبههای مختلف محیطی دارد [7]. هیچ ساختار منفردی بهتنهایی تعادل ایستا را تحت پوشش قرار نمیدهد، بلکه کنترل تعادل ایستا نتیجه اثر متقابل سیستمهای عضلانی، اسکلتی و عصبی است [7].
یکی از اجزای سیستم عصبی در کنترل تعادل ایستا، سیستمهای حسی است که برای درک موقعیت بدن در فضا باید اطلاعات دریافتی از گیرندههای حسی سیستمهای بینایی، سوماتوسنسوری (گیرندههای پوستی، مفاصل و عضلات)، وستیبولار و شنوایی را پردازش و سازماندهی کند. هر یک از این سیستمها به عنوان یک مرجع اطلاعاتی ویژه، اطلاعات خاصی را از وضعیت بدن در اختیار سیستم اعصاب مرکزی قرار میدهند [7].
سیستم سوماتوسنسوری اطلاعات مربوط به وضعیت بدن نسبت به سطح اتکا و ارتباط اجزای مختلف بدن نسبت به همدیگر را برای سیستم اعصاب مرکزی فراهم میکند. سیستم بینایی اطلاعات مربوط به وضعیت و حرکت سر را نسبت به اشیای موجود در محیط گزارش میدهد. اطلاعات سیستم وستیبولار منبع مهمی برای درک وضعیت و حرکت سر در ارتباط با نیروی جاذبه است [8]. گیرندههای شنوایی مسئول آگاهسازی فرد از ماهیت حرکات در محیط هستند [9 ،6]؛ به طوری که پاسخ بیش از حد به محرکهای شنیداری ممکن است به تغییر تون عضلانی منتهی شود که اغلب در کنترل حالت بدن و هماهنگی پاسخهای حرکتی مؤثر است [10 ،6]. این محرکات میتوانند به صورت قابل پیشبینی و غیر قابل پیشبینی ظاهر شوند و سبب فعال شدن سیستم دستگاه عصبی خودکار و بروز اختلال در حفظ تعادل ایستا شوند [11 ،6]. این اختلال میتواند به دو صورت حرکتی و شناختی بر عملکرد تعادلی فرد مؤثر باشد، تأثیرات حرکتی با افزایش تون عضلانی و بروز رفلکسهایی نظیر استارتل و مورو و تأثیرات شناختی با دشواری در توجه وتمرکز مشخص میشود [13-11].
کودکان فلج مغزی اسپاستیک تجربه کمی در رد (فیلتریشن) محرکات نامربوط دارند. توجه کارکردی آنها حین انجام تکالیف حرکتی با بیشترین محدودیت همراه است و نیاز به توجه اختصاصی برای انجام عملکردهای شناختی حین کنترل تعادل ایستا دارند [11]. در محیطهای پرمحرک مشکلات تعادل ایستا در کودکان فلج مغزی افزایش مییابد. از آنجایی که حفظ تعادل به تأثیر و کارآمدی پیشخوراندهایی از دروندادهای حسی متنوع وابسته است، اهمیت دروندادهای شنیداری از این لحاظ هنوز کاملاً مشخص نشده است [13 ،11].
با وجود آنکه اختلال درکنترل تعادل ایستا یکی از مشخصههای اصلی فلج مغزی و به عنوان عامل اصلی اختلال در کارکرد این کودکان مطرح است، مطالعات محدودی درباره روشهای بهبود کنترل تعادل ایستا در این کودکان صورت گرفته است [15 ،14]. برنامههای درمانی بیشتر در حوزههای اسبدرمانی [17 ،16]، آبدرمانی [18]، تکالیف دوگانه [20 ،19]، تردمیل [22 ،21] و چند برنامه تقویتی بود [24 ،23]. در بیشتر مطالعات تکالیف دوگانه به بررسی تداخل برنامههای شناختی [20] یا برنامههایی با تأکید بر حافظه کاری بینایی و کنترل تعادل ایستا پرداخته شده است [19].
با توجه به علائم گسترده در این کودکان، ضرورت اجرای مداخلات درمانی متعدد، تحقیقات محدود در حوزه تأثیر تحریکات شنیداری در تعادل کودکان فلج مغزی، و نقصان نتایج قطعی پیرامون ارتباط بین تعادل ایستا و تحریکات شنیداری، لزوم اجرای این پژوهش ضروری به نظر رسید. هدف از اجرای پژوهش، بررسی تأثیر تحریک شنیداری ناملایم با شدت متفاوت و سطح اتکا بر تعادل ایستای کودکان فلج مغزی اسپاستیک5 تا 12 ساله است.
روش بررسی
این تحقیق از نوع توصیفی تحلیلی بود که روی 20 کودک اسپاستیک 5 تا 12 سال شهر تهران انجام شد. برای محاسبه حجم نمونه، مقدار انحراف معیار در مطالعهای مشابه بررسی شد. حجم نمونه با استفاده از انحراف معیار با فرمول زیر محاسبه شد. در این فرمول انحراف معیار 0/15، z (ضریب اطمینان 95 درصد) 2/8، دقت احتمالی مطلوب d] 0/1 ]در نظر گرفته شده است.
روش نمونهگیری از نوع در دسترس آسان بود. کودکانی با تشخیص فلج مغزی توسط متخصص مغز و اعصاب ،دامنه سنی 5 تا 12 سال، توانایی ایستادن مستقل حداقل به مدت 30 ثانیه، میزان اسپاستیسیتی 1 تا 3 در مچ پا بر اساس مقیاس اصلاحشده آشورث [14] ، نداشتن آسیب بینایی (نیستاگموس، استرابیسم) با تأیید متخصص مغز و اعصاب یا چشم پزشک، شرکت نکردن در برنامه مداخلهای مشابه با برنامههای مداخلهای در این طرح و نداشتن آسیب به عصب هشتم مغزی با تأیید متخصص گوش وحلق و بینی و شنواییشناس و داشتن هوشبهر بالای 70 بر اساس پرسشنامه اسپارکل وارد مطالعه میشدند. ابزار استفادهشده در این مطالعه شامل پرسشنامه دموگرافیک، معیار تعدیلیافته آشورث، پرسشنامه اسپارکل و صفحه نیرو بودند.
معیار تعدیلیافته آشورث برای ارزیابی میزان اسپاستیسیتی عضلات به کار میرود. در مقیاس تعدیلیافته آشورث اندام با سرعت ثابت در دامنه کامل حرکت داده میشود و قوام از نمره صفر (هنجار) تا چهار (غیر قابل حرکت) درجهبندی میشود. روایی و پایایی این معیار در مطالعه موتلو و همکاران تأیید شده است [25]. این اندازهگیری در محیطی آرام انجام گرفت در حالی که بیمار نشسته بود. اندازهگیری برای هر کودک سه بار تکرار شد و بهترین نمره بهدستآمده در سمت درگیرتر ثبت شد. نمرهدهی به این شرح بود: افزایش نیافتن قوام عضله: 1. افزایش خفیف قوام عضله با حداقل مقاومت در انتهای دامنه حرکتی در حین حرکت فلکسیون یا اکستانسیون بخش مبتلا، افزایش خفیف قوام عضله یا گیر کردن با حداقل مقاومت در کمتر از نصف دامنه حرکتی؛ 2. افزایش قابل ملاحظه قوام عضله در حدی که بخش مبتلا بهراحتی حرکت کند؛ 3. افزایش قابل ملاحظه قوام عضله در حدی که انجام حرکت پاسیو دشوار باشد؛ 4. سفتی بخشهای مبتلا در فلکسیون و اکستانسیون.
آلن کولور و گروه اسپارکل پرسشنامه اسپارکل را به منظور ارزیابی تخمینی سطح شناختی کودکان طراحی کردند که خانوادهها آن را تکمیل میکنند و بهره هوشی کودکان را در سه سطح (زیر 50، بین 50 تا 70، و بالای 70) طبقهبندی میکند. این پرسشنامه شامل 6 سؤال است [26].
برای ثبت اطلاعات مربوط به متغیرهای تعادل از دستگاه صفحه نیرو مدل 9286A کیستلر ساخت کشور سوئیس تحت نرمافزار 12-0-Bioware 4 موجود در آزمایشگاه ارگونومی دانشگاه علوم بهزیستی و توانبخشی استفاده شد. صفحه نیرو ازجمله تجهیزات آزمایشگاه بیومکانیک است که به اندازهگیری نیروهای عکسالعمل زمین به کف پای فرد و ثبت اجزای بیومکانیک تعادل ایستا و پویا میپردازد [27]. این صفحه نیرو چهار حسگر در چهار گوشه صفحه مستطیلشکل 60×90 سانتیمتری دارد. از آنجایی که حسگرهای این دستگاه از نوع پیزو الکتریک 8 است با هر بار ایستادن روی دستگاه، کالیبریشن خودبهخود انجام میشد.
هر کودک با پای برهنه در حالی که دستهایش کنار بدنش بود، روی نقاط نشاندارشده به مدت 30 ثانیه روی صفحه نیرو میایستاد که یکبار با پوشش سخت و یکبار با پوشش نرم فرش میشد و به عکس منظرهای نگاه میکرد که در فاصله دو متری و دقیقاً روبهروی او قرار داشت. سپس تحریک شنیداری ناملایم با دو شدت متفاوت (کم و زیاد) که بر اساس نتایج تست آستانه دردناکی شنیداری توسط ادیولوژیست طراحی شده بود، از پشت سر کودک از طریق اسپیکری که در فاصله 50 سانتیمتری او قرار داشت پخش میشد. چهار تکلیف شامل ایستادن روی سطح نرم با تحریک شنیداری ناملایم شدت بالا، ایستادن روی سطح نرم با تحریک شنیداری ناملایم شدت پایین، ایستادن روی سطح سخت با تحریک شنیداری ناملایم شدت بالا، و ایستادن روی سطح سخت با تحریک شنیداری ناملایم شدت پایین بود.
مدت زمان انجام هر تکلیف 30 ثانیه بود و سه بار تکرار میشد.کودک اجازه داشت در فواصل مناسب (بعد از هر سه بار تکرار) بین تکالیف استراحت کند. دادهها برای هر کودک سه بار، هر بار به مدت 30 ثانیه و با فرکانس 100 هرتز ثبت شد. دادهها در نرمافزار متلب نسخه R2010a تحت فیلتر پایینگذر پردازش شدند. سپس برای مقایسه تأثیر تحریک شنیداری ناملایم در شدتهای بالا و پایین بر سطوح نرم و سخت با چشم باز و در حالت ایستاده بدون حرکت، سرعت جابهجایی و تصویر سطح پایه در صفحه قدامی خلفی به روش آماری t زوجی در نرمافزار spss نسخه 16 تجزیهوتحلیل شدند. منظور از تصویر سطح پایه، انحراف معیار مجموع واریانس سرعت و نوسان است [28]. کمیته اخلاق دانشگاه علوم بهزیستی و توانبخشی این مطالعه را تأیید کرده است.
یافتهها
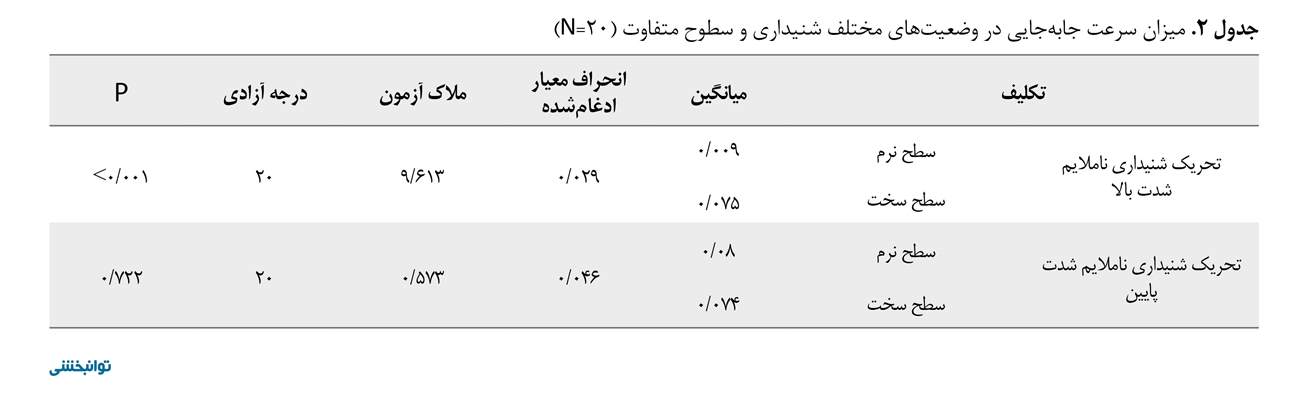
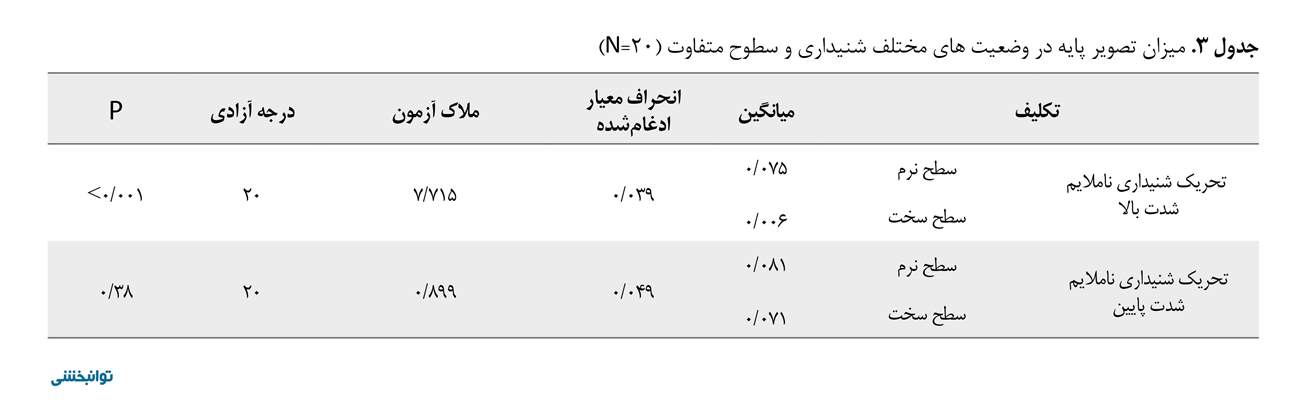
مطالعه حاضر روی 20 کودک مبتلا به فلج مغزی با میانگین سنی 2/03±7/10 سال در سطوح 1 و 2 سیستم طبقهبندی عملکرد حرکتی درشت انجام شد. 75 درصد از شرکتکنندگان در سطح II سیستم طبقه بندی عملکرد حرکتی درشت و شدت اسپاستیسیتی در 60 درصد از آنان در سطح یک معیار آشورث تعدیل یافته بود (جدول شماره 1). بر اساس آزمون شاپیرو ویلک متغیرها توزیع نرمال داشتند. همانگونه که در جدول شماره 1 مشاهده میشود، تحریک شنیداری ناملایم با شدت بالا روی سرعت جابهجایی در صفحه قدامی خلفی معنادار بود (0/001P) (جدول شماره 2). همچنین تحریک شنیداری ناملایم با شدت بالا روی تصویر سطح پایه در صفحه قدامی خلفی معنادار بود ( 0/001P) (جدول شماره 3).
معیار تعدیلیافته آشورث برای ارزیابی میزان اسپاستیسیتی عضلات به کار میرود. در مقیاس تعدیلیافته آشورث اندام با سرعت ثابت در دامنه کامل حرکت داده میشود و قوام از نمره صفر (هنجار) تا چهار (غیر قابل حرکت) درجهبندی میشود. روایی و پایایی این معیار در مطالعه موتلو و همکاران تأیید شده است [25]. این اندازهگیری در محیطی آرام انجام گرفت در حالی که بیمار نشسته بود. اندازهگیری برای هر کودک سه بار تکرار شد و بهترین نمره بهدستآمده در سمت درگیرتر ثبت شد. نمرهدهی به این شرح بود: افزایش نیافتن قوام عضله: 1. افزایش خفیف قوام عضله با حداقل مقاومت در انتهای دامنه حرکتی در حین حرکت فلکسیون یا اکستانسیون بخش مبتلا، افزایش خفیف قوام عضله یا گیر کردن با حداقل مقاومت در کمتر از نصف دامنه حرکتی؛ 2. افزایش قابل ملاحظه قوام عضله در حدی که بخش مبتلا بهراحتی حرکت کند؛ 3. افزایش قابل ملاحظه قوام عضله در حدی که انجام حرکت پاسیو دشوار باشد؛ 4. سفتی بخشهای مبتلا در فلکسیون و اکستانسیون.
آلن کولور و گروه اسپارکل پرسشنامه اسپارکل را به منظور ارزیابی تخمینی سطح شناختی کودکان طراحی کردند که خانوادهها آن را تکمیل میکنند و بهره هوشی کودکان را در سه سطح (زیر 50، بین 50 تا 70، و بالای 70) طبقهبندی میکند. این پرسشنامه شامل 6 سؤال است [26].
برای ثبت اطلاعات مربوط به متغیرهای تعادل از دستگاه صفحه نیرو مدل 9286A کیستلر ساخت کشور سوئیس تحت نرمافزار 12-0-Bioware 4 موجود در آزمایشگاه ارگونومی دانشگاه علوم بهزیستی و توانبخشی استفاده شد. صفحه نیرو ازجمله تجهیزات آزمایشگاه بیومکانیک است که به اندازهگیری نیروهای عکسالعمل زمین به کف پای فرد و ثبت اجزای بیومکانیک تعادل ایستا و پویا میپردازد [27]. این صفحه نیرو چهار حسگر در چهار گوشه صفحه مستطیلشکل 60×90 سانتیمتری دارد. از آنجایی که حسگرهای این دستگاه از نوع پیزو الکتریک 8 است با هر بار ایستادن روی دستگاه، کالیبریشن خودبهخود انجام میشد.
هر کودک با پای برهنه در حالی که دستهایش کنار بدنش بود، روی نقاط نشاندارشده به مدت 30 ثانیه روی صفحه نیرو میایستاد که یکبار با پوشش سخت و یکبار با پوشش نرم فرش میشد و به عکس منظرهای نگاه میکرد که در فاصله دو متری و دقیقاً روبهروی او قرار داشت. سپس تحریک شنیداری ناملایم با دو شدت متفاوت (کم و زیاد) که بر اساس نتایج تست آستانه دردناکی شنیداری توسط ادیولوژیست طراحی شده بود، از پشت سر کودک از طریق اسپیکری که در فاصله 50 سانتیمتری او قرار داشت پخش میشد. چهار تکلیف شامل ایستادن روی سطح نرم با تحریک شنیداری ناملایم شدت بالا، ایستادن روی سطح نرم با تحریک شنیداری ناملایم شدت پایین، ایستادن روی سطح سخت با تحریک شنیداری ناملایم شدت بالا، و ایستادن روی سطح سخت با تحریک شنیداری ناملایم شدت پایین بود.
مدت زمان انجام هر تکلیف 30 ثانیه بود و سه بار تکرار میشد.کودک اجازه داشت در فواصل مناسب (بعد از هر سه بار تکرار) بین تکالیف استراحت کند. دادهها برای هر کودک سه بار، هر بار به مدت 30 ثانیه و با فرکانس 100 هرتز ثبت شد. دادهها در نرمافزار متلب نسخه R2010a تحت فیلتر پایینگذر پردازش شدند. سپس برای مقایسه تأثیر تحریک شنیداری ناملایم در شدتهای بالا و پایین بر سطوح نرم و سخت با چشم باز و در حالت ایستاده بدون حرکت، سرعت جابهجایی و تصویر سطح پایه در صفحه قدامی خلفی به روش آماری t زوجی در نرمافزار spss نسخه 16 تجزیهوتحلیل شدند. منظور از تصویر سطح پایه، انحراف معیار مجموع واریانس سرعت و نوسان است [28]. کمیته اخلاق دانشگاه علوم بهزیستی و توانبخشی این مطالعه را تأیید کرده است.
یافتهها
مطالعه حاضر روی 20 کودک مبتلا به فلج مغزی با میانگین سنی 2/03±7/10 سال در سطوح 1 و 2 سیستم طبقهبندی عملکرد حرکتی درشت انجام شد. 75 درصد از شرکتکنندگان در سطح II سیستم طبقه بندی عملکرد حرکتی درشت و شدت اسپاستیسیتی در 60 درصد از آنان در سطح یک معیار آشورث تعدیل یافته بود (جدول شماره 1). بر اساس آزمون شاپیرو ویلک متغیرها توزیع نرمال داشتند. همانگونه که در جدول شماره 1 مشاهده میشود، تحریک شنیداری ناملایم با شدت بالا روی سرعت جابهجایی در صفحه قدامی خلفی معنادار بود (0/001
بحث
در این مطالعه نتایج حاصل از تجزیهوتحلیل دادهها نشان داد میانگین عملکرد تعادلی کودکان مبتلا به فلج مغزی حین انجام تحریک شنیداری ناملایم (شدت بالا)، با چشم باز روی سطح نرم یا سخت متفاوت بوده است. مطالعه هاتزیتاکی و همکاران در سال 2002 نشان داد بین درک حرکتی با کنترل تعادل ایستا و پویا در کودکان رابطه معناداری وجود دارد، به طوری که میزان مرکز فشار در محور قدامی خلفی و داخلی خارجی در مدت زمان 5 ثانیه به حداکثر مقدار خود میرسد [29].
واک و همکاران در سال 2007 در مطالعهای تأثیر تحریکات شنیداری ریتمیک را روی عملکردهای راه رفتن 25 فرد مبتلا به فلج مغزی اسپاستیک 6 تا 25 سال با توانایی راه رفتن بررسی کردند. شرکتکنندگان درسه گروه کنترل،گروه با هدایت درمانگر و گروه خودکنترل تقسیم شدند. از شرکتکنندگان خواسته شد در مسافت 10 متری به ترتیب دو متر را باشتاب و دو متر را کمشتاب در حین پخش سه موزیک جاز، مارش و ملایم راه بروند.
پس از سه هفته نتایج بدین شرح بود که پهنای گام در هر سه گروه بهبود معنیداری داشت، اما تنها درگروه با هدایت درمانگر تفاوت معنیداری در شتاب و قرینگی دیده شد. گرچه تفاوت درونگروهی درگروه خودکنترل دیده شد، اما این تغییر به اندازه گروه باهدایت درمانگر درسطوح خودانگیزشی گزارش نشد [11]. نتایج مطالعات واک و همکاران نشان داد تحریکات شنیداری ریتمیک روی عملکردهای راه رفتن کودکان فلج مغزی مؤثر بوده است. آنان معتقد بودند فاکتورهای شخصی نظیر عملکرد شناختی، قابلیتهای جسمانی و حمایت والدین و مراقبان، نقش مهمی در طراحی و آموزش کاربردی در این زمینه دارد [11]. گرچه واک و همکارانش در این مطالعه الگوهای راه رفتن کودکان و فاکتورهای فردی و شخصی (تاریخچه جراحی، شکستگی، کانترکچرها و ...) افراد را اندازهگیری نکرده بودند.
تزادل و همکاران در سال 2001 در مطالعهای تأثیر قطع و برقراری مجدد اطلاعات حسی را بر کنترل وضعیت بررسی کردند [30]. از اینرو 16 آزمودنی در دو گروه سنی با میانگین سنی گروه اول 24/8 سال و گروه دوم 68 سال به مدت 25 ثانیه در حالی که هر یک از حالات حذف و برقراری مجدد حسهای بینایی و عمقی را تجربه میکردند، روی صفحه نیرو میایستادند. آزمودنیها باید به یک تحریک شنیداری غیرمنتظره به صورت شفاهی پاسخ میدادند.
نتیجه مطالعه نشان داد در زمان برقراری مجدد اطلاعات حسی عمقی هر دو گروه سنی با افزایش سرعت جابهجایی مرکز فشار مواجه شدند که در سالمندان بیشتر بود و بعد از گذشت 10 ثانیه سرعت کاهش یافت. اما در حالت چشمبسته بازگشت سرعت جابهجایی مرکز فشار به میزان پایه وجود نداشت؛ به عبارتی با وجود دروندادهای بینایی آزمودنیها توانستند در زمان 10 ثانیه با وزنگذاری مجدد دروندادهای حسی و برقراری مجدد حس عمقی، موجب افزایش نیاز به توجه در فرایند کنترل تعادل ایستا شوند که این حالت در سالمندان بارزتر بود [30]. محققان علت این تغییرات را اهمیت ویژه دروندادهای حس عمقی در فرایند کنترل تعادل ایستا دانستهاند. در واقع با حذف اطلاعات بینایی فرد با کاهش کثرت اطلاعات حسی روبهرو میشود که عاملی برای افزایش نیازهای توجهی کنترل تعادل ایستا محسوب میشود [13].
نتایج مطالعه حاضر نشان داد کودکان فلج مغزی بیشترین مشکلات را در ایستادن و انجام همزمان تکلیف دیگر روی سطح نرم در مقایسه با سطح سخت نشان میدهند. بسیاری از مشکلات تعادل ایستا تحت تأثیر مشکلات تعادلی و بسیاری تحت تأثیر عوامل محیطی است [11]. محققان به این نتیجه دست یافتند که تنظیم ثبات وضعیت تنها به عوامل محیطی وابسته نیست و به توانایی هر فرد در پردازش اطلاعات نیز وابسته است [32 ،31 ،19 ،11]. در واقع تحریک شنیداری تأثیر ناپایداری روی کنترل وضعیت دارد و تحت تأثیر عوامل مختلفی قرار میگیرد؛ مثل: سن افراد، وضعیت فیزیولوژیکی، نوع تحریک ارائهشده به آزمودنی و نوع تکلیف تعادلی و وضعیت تکلیف ثانویه (تکلیف شناختی) [32 ،31 ،19 ،11]. به نظر میرسد دلیل متفاوت بودن نتایج مطالعه حاضر نیز همین عوامل باشد.
سیستم حسی پیکری، سیستم مرکزی را با اطلاعات وضعیت و حرکت بدن با توجه به سطح اتکا تجهیز میکند [7 ،5]؛ به علاوه دروندادهای سراسر بدن و وضعیت سگمانهای بدنی نسبت به هم را نیز به مغز مخابره میکند. در شرایط طبیعی، هنگام ایستادن روی سطحی سخت و صاف، گیرندههای حسی پیکری، فراهمکننده اطلاعاتی درباره وضعیت و حرکت بدن با توجه به سطح افق هستند. در حالی که اگر فردی روی سطحی که نسبت به بدنش متحرک است یا سطحی بایستد که در راستای افقی نیست، این حس دیگر نمیتواند درک صحیحی از موقعیت افقی بدن داشته باشد. در این شرایط حس سوماتوسنسوری موقعیت بدن را تشخیص نمیدهد و اطلاعات دریافتی از آن قابل اعتماد و مفید نیست [7 ،5]. متفاوت بودن نتایج حاصل از مطالعه شاید به دلیل شرایط سنی شرکتکنندگان و پیچیدگی استراتژیهای کنترل وضعیت در این سن باشد. بنابراین پیشنهاد میشود مطالعات بعدی تأثیر تحریک شنیداری در وضعیتهای دشوار تعادلی و مدت زمان واکنش در حین دادن تحریکات شنیداری را بررسی کند.
نتیجهگیری
نتایج حاصل از مطالعه حاضر نشان داد میانگین عملکرد تعادلی کودکان مبتلا به فلج مغزی تحت تأثیر تحریک شنیداری ناملایم با شدت متفاوت (بالا و پایین) و جنس سطح اتکا (نرم یا سخت) متفاوت است. به طوری که تحریک شنیداری ملایم با شدت پایین تأثیری در بر هم خوردن تعادل ندارد. بنابراین در نظر داشتن این عوامل در طراحی، برنامه مداخلهای تکلیف دوگانه بر مبنای تحریک شنیداری و یا انجام مطالعاتی در خصوص استفاده از رویکرد یکپارچگی حسی و کنترل حرکتی و بهبود کنترل تعادل ایستا مفید است.
ملاحظات اخلاقی
پیروی از اصول اخلاق پژوهش
در این مطالعه اصول اخلاقی لازم در پژوهشهای علمی رعایت شد. پس از ارئه توضیحات کافی در خصوص نحوه اجرای مطالعه، از والدین کودکان واجد شرایط برای ورود به مطالعه رضایت کتبی گرفته شد. به والدین کودکان اطمینان داده شد اطلاعات مربوط به آنان محرمانه باقی خواهد ماند. محققان متعهد شدند گرچه این مداخله هیچ عوارضی ندارد، اما در صورت بروز هر مشکلی در روند مطالعه مسئول حل مشکل به شکل رایگان خواهند بود. این مطالعه هیچ هزینه مالی برای شرکتکنندگان نداشت.
حامی مالی
این مقاله از پایاننامه کارشناسی ارشد خانم معصومه اسماعیلپور نوسر در گروه کاردرمانی دانشگاه علوم بهزیستی و توانبخشی به راهنمایی جناب آقای دکتر سید علی حسینی و سرکار خانم دکتر نازیلا اکبر فهیمی گرفته شده است. این مقاله حامی مالی ندارد.
تعارض منافع
بنابر اظهار نویسندگان این مقاله تعارض منافع ندارد.
تشکر و قدردانی
بدینوسیله از تمام کسانی که در انجام این تحقیق ما را یاری کردند و همچنین سرکار خانم مهندس هدی نبوی، مسئول آزمایشگاه ارگونومی دانشگاه علوم بهزیستی و توانبخشی برای حمایت و اجرای آزمون تشکر و قدردانی میشود.
در این مطالعه نتایج حاصل از تجزیهوتحلیل دادهها نشان داد میانگین عملکرد تعادلی کودکان مبتلا به فلج مغزی حین انجام تحریک شنیداری ناملایم (شدت بالا)، با چشم باز روی سطح نرم یا سخت متفاوت بوده است. مطالعه هاتزیتاکی و همکاران در سال 2002 نشان داد بین درک حرکتی با کنترل تعادل ایستا و پویا در کودکان رابطه معناداری وجود دارد، به طوری که میزان مرکز فشار در محور قدامی خلفی و داخلی خارجی در مدت زمان 5 ثانیه به حداکثر مقدار خود میرسد [29].
واک و همکاران در سال 2007 در مطالعهای تأثیر تحریکات شنیداری ریتمیک را روی عملکردهای راه رفتن 25 فرد مبتلا به فلج مغزی اسپاستیک 6 تا 25 سال با توانایی راه رفتن بررسی کردند. شرکتکنندگان درسه گروه کنترل،گروه با هدایت درمانگر و گروه خودکنترل تقسیم شدند. از شرکتکنندگان خواسته شد در مسافت 10 متری به ترتیب دو متر را باشتاب و دو متر را کمشتاب در حین پخش سه موزیک جاز، مارش و ملایم راه بروند.
پس از سه هفته نتایج بدین شرح بود که پهنای گام در هر سه گروه بهبود معنیداری داشت، اما تنها درگروه با هدایت درمانگر تفاوت معنیداری در شتاب و قرینگی دیده شد. گرچه تفاوت درونگروهی درگروه خودکنترل دیده شد، اما این تغییر به اندازه گروه باهدایت درمانگر درسطوح خودانگیزشی گزارش نشد [11]. نتایج مطالعات واک و همکاران نشان داد تحریکات شنیداری ریتمیک روی عملکردهای راه رفتن کودکان فلج مغزی مؤثر بوده است. آنان معتقد بودند فاکتورهای شخصی نظیر عملکرد شناختی، قابلیتهای جسمانی و حمایت والدین و مراقبان، نقش مهمی در طراحی و آموزش کاربردی در این زمینه دارد [11]. گرچه واک و همکارانش در این مطالعه الگوهای راه رفتن کودکان و فاکتورهای فردی و شخصی (تاریخچه جراحی، شکستگی، کانترکچرها و ...) افراد را اندازهگیری نکرده بودند.
تزادل و همکاران در سال 2001 در مطالعهای تأثیر قطع و برقراری مجدد اطلاعات حسی را بر کنترل وضعیت بررسی کردند [30]. از اینرو 16 آزمودنی در دو گروه سنی با میانگین سنی گروه اول 24/8 سال و گروه دوم 68 سال به مدت 25 ثانیه در حالی که هر یک از حالات حذف و برقراری مجدد حسهای بینایی و عمقی را تجربه میکردند، روی صفحه نیرو میایستادند. آزمودنیها باید به یک تحریک شنیداری غیرمنتظره به صورت شفاهی پاسخ میدادند.
نتیجه مطالعه نشان داد در زمان برقراری مجدد اطلاعات حسی عمقی هر دو گروه سنی با افزایش سرعت جابهجایی مرکز فشار مواجه شدند که در سالمندان بیشتر بود و بعد از گذشت 10 ثانیه سرعت کاهش یافت. اما در حالت چشمبسته بازگشت سرعت جابهجایی مرکز فشار به میزان پایه وجود نداشت؛ به عبارتی با وجود دروندادهای بینایی آزمودنیها توانستند در زمان 10 ثانیه با وزنگذاری مجدد دروندادهای حسی و برقراری مجدد حس عمقی، موجب افزایش نیاز به توجه در فرایند کنترل تعادل ایستا شوند که این حالت در سالمندان بارزتر بود [30]. محققان علت این تغییرات را اهمیت ویژه دروندادهای حس عمقی در فرایند کنترل تعادل ایستا دانستهاند. در واقع با حذف اطلاعات بینایی فرد با کاهش کثرت اطلاعات حسی روبهرو میشود که عاملی برای افزایش نیازهای توجهی کنترل تعادل ایستا محسوب میشود [13].
نتایج مطالعه حاضر نشان داد کودکان فلج مغزی بیشترین مشکلات را در ایستادن و انجام همزمان تکلیف دیگر روی سطح نرم در مقایسه با سطح سخت نشان میدهند. بسیاری از مشکلات تعادل ایستا تحت تأثیر مشکلات تعادلی و بسیاری تحت تأثیر عوامل محیطی است [11]. محققان به این نتیجه دست یافتند که تنظیم ثبات وضعیت تنها به عوامل محیطی وابسته نیست و به توانایی هر فرد در پردازش اطلاعات نیز وابسته است [32 ،31 ،19 ،11]. در واقع تحریک شنیداری تأثیر ناپایداری روی کنترل وضعیت دارد و تحت تأثیر عوامل مختلفی قرار میگیرد؛ مثل: سن افراد، وضعیت فیزیولوژیکی، نوع تحریک ارائهشده به آزمودنی و نوع تکلیف تعادلی و وضعیت تکلیف ثانویه (تکلیف شناختی) [32 ،31 ،19 ،11]. به نظر میرسد دلیل متفاوت بودن نتایج مطالعه حاضر نیز همین عوامل باشد.
سیستم حسی پیکری، سیستم مرکزی را با اطلاعات وضعیت و حرکت بدن با توجه به سطح اتکا تجهیز میکند [7 ،5]؛ به علاوه دروندادهای سراسر بدن و وضعیت سگمانهای بدنی نسبت به هم را نیز به مغز مخابره میکند. در شرایط طبیعی، هنگام ایستادن روی سطحی سخت و صاف، گیرندههای حسی پیکری، فراهمکننده اطلاعاتی درباره وضعیت و حرکت بدن با توجه به سطح افق هستند. در حالی که اگر فردی روی سطحی که نسبت به بدنش متحرک است یا سطحی بایستد که در راستای افقی نیست، این حس دیگر نمیتواند درک صحیحی از موقعیت افقی بدن داشته باشد. در این شرایط حس سوماتوسنسوری موقعیت بدن را تشخیص نمیدهد و اطلاعات دریافتی از آن قابل اعتماد و مفید نیست [7 ،5]. متفاوت بودن نتایج حاصل از مطالعه شاید به دلیل شرایط سنی شرکتکنندگان و پیچیدگی استراتژیهای کنترل وضعیت در این سن باشد. بنابراین پیشنهاد میشود مطالعات بعدی تأثیر تحریک شنیداری در وضعیتهای دشوار تعادلی و مدت زمان واکنش در حین دادن تحریکات شنیداری را بررسی کند.
نتیجهگیری
نتایج حاصل از مطالعه حاضر نشان داد میانگین عملکرد تعادلی کودکان مبتلا به فلج مغزی تحت تأثیر تحریک شنیداری ناملایم با شدت متفاوت (بالا و پایین) و جنس سطح اتکا (نرم یا سخت) متفاوت است. به طوری که تحریک شنیداری ملایم با شدت پایین تأثیری در بر هم خوردن تعادل ندارد. بنابراین در نظر داشتن این عوامل در طراحی، برنامه مداخلهای تکلیف دوگانه بر مبنای تحریک شنیداری و یا انجام مطالعاتی در خصوص استفاده از رویکرد یکپارچگی حسی و کنترل حرکتی و بهبود کنترل تعادل ایستا مفید است.
ملاحظات اخلاقی
پیروی از اصول اخلاق پژوهش
در این مطالعه اصول اخلاقی لازم در پژوهشهای علمی رعایت شد. پس از ارئه توضیحات کافی در خصوص نحوه اجرای مطالعه، از والدین کودکان واجد شرایط برای ورود به مطالعه رضایت کتبی گرفته شد. به والدین کودکان اطمینان داده شد اطلاعات مربوط به آنان محرمانه باقی خواهد ماند. محققان متعهد شدند گرچه این مداخله هیچ عوارضی ندارد، اما در صورت بروز هر مشکلی در روند مطالعه مسئول حل مشکل به شکل رایگان خواهند بود. این مطالعه هیچ هزینه مالی برای شرکتکنندگان نداشت.
حامی مالی
این مقاله از پایاننامه کارشناسی ارشد خانم معصومه اسماعیلپور نوسر در گروه کاردرمانی دانشگاه علوم بهزیستی و توانبخشی به راهنمایی جناب آقای دکتر سید علی حسینی و سرکار خانم دکتر نازیلا اکبر فهیمی گرفته شده است. این مقاله حامی مالی ندارد.
تعارض منافع
بنابر اظهار نویسندگان این مقاله تعارض منافع ندارد.
تشکر و قدردانی
بدینوسیله از تمام کسانی که در انجام این تحقیق ما را یاری کردند و همچنین سرکار خانم مهندس هدی نبوی، مسئول آزمایشگاه ارگونومی دانشگاه علوم بهزیستی و توانبخشی برای حمایت و اجرای آزمون تشکر و قدردانی میشود.
References
- Rosenbaum P, Paneth N, Leviton A, Goldstein M, Bax M, Damiano D, et al. A report: The definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology. 2007; 109:8-14. [PMID]
- Odding E, Roebroeck ME, Stam HJ. The epidemiology of cerebral palsy: Incidence, impairments and risk factors. Journal Disability and Rehabilitation. 2006; 28(4):183-91. [DOI:10.1080/09638280500158422 ] [PMID]
- Case-Smith J, O’Brien JC. Occupational therapy for children and adolescents. New York: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2014.
- Soleimani F, Vameghi R, Rassafiani M, Akbar Fahimi N, Nobakht Z. Cerebral palsy: Motor types, gross motor function and associated disorders. Iranian Rehabilitation Journal. 2011; 9:21-31.
- Akbar Fahimi N, Hosseini SA, Rassafiani M, Farzad M, Haghgoo HA. The reactive postural control in spastic cerebral palsy children. Iranian Rehabilitation Journal. 2012; 10(1):66-74.
- Melzer I, Damry E, Landau A, Yagev R. The influence of an auditory–memory attention-demanding task on postural control in blind persons. Clinical Biomechanics. 2011; 26(4):358-62. [DOI:10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2010.11.008] [PMID]
- Shumway-Cook A, Woollacott MH. Motor control: Translating research into clinical practice. Philadephia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007.
- Maurer C, Mergner T, Bolha B, Hlavacka F. Vestibular, visual, and somatosensory contributions to human control of upright stance. Neuroscience Letters. 2000; 281(2-3):99-102. [DOI:10.1016/S0304-3940(00)00814-4]
- Shumway-Cook A, Woollacott M. Attentional demands and postural control: The effect of sensorycontext. Journals of Gerontology-Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2000; 55(1):M10-16. [DOI:10.1093/gerona/55.1.M10]
- Magnusson M, Johansson K, Johansson BB. Sensory stimulation promotes normalization of postural control after stroke. Stroke. 1994; 25(6):1176-80. [DOI:10.1161/01.STR.25.6.1176] [PMID]
- Kwak EE. Effect of rhythmic auditory stimulation on gait performance in children with spastic cerebral palsy. Journal of Music Therapy. 2007; 44(3):198-216. [DOI:10.1093/jmt/44.3.198] [PMID]
- Nobahar Ahari M, Nejati V, Hosseini SA. Attentional Demands of balance under Dual Task conditions in young adults. Iranian Rehabilitation Journal. 2012; 10(16):66-71.
- Melzer I, Benjuya N, Kaplanski J. Age-related changes of postural control: Effect of cognitive tasks. Gerontology. 2001; 47(4):189-94. [DOI:10.1159/000052797] [PMID]
- Shumway-Cook A, Hutchinson S, Kartin D, Price R, Woollacott M. Effect of balance training on recovery of stability in children with cerebral palsy. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology. 2003; 45(9):591-602. [DOI:10.1017/S0012162203001099] [PMID]
- Novak I, Mcintyre S, Morgan C, Campbell L, Dark L, Morton N, et al. A systematic review of interventions for children with cerebral palsy: State of the evidence. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology. 2013; 55(10):885-910. [DOI:10.1111/dmcn.12246] [PMID]
- Champagne D, Corriveau H, Dugas C. Effect of hippotherapy on motor proficiency and function in children with cerebral palsy who walk. Physical & Occupational Therapy in Pediatrics. 2017; 37(1):51-63. [DOI:10.3109/01942638.2015.1129386] [PMID]
- Deutz U, Heussen N, Weigt-Usinger K, Leiz S, Raabe C, Polster T, et al. Impact of hippotherapy on gross motor function and quality of life in children with bilateral cerebral palsy: A randomized open-label crossover study. Thieme E-Books & E-Journals-Neuropediatrics. 2018; 49(3):185-92. [DOI:10.1055/s-0038-1635121] [PMID]
- Gorter JW, Currie SJ. Aquatic exercise programs for children and adolescents with Cerebral Palsy: What do we know and where do we go. International Journal of Pediatrics. 2011; 2011: 712165. [DOI: 10.1155/2011/712165] [PMID] [PMCID]
- Reilly DS, Woollacott MH, van Donkelaar P, Saavedra S. The interaction between executive attention and postural control in dual-task conditions: children with cerebral palsy. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2008; 89(5):834-42. [DOI:10.1016/j.apmr.2007.10.023] [PMID]
- Samuel A, Solomon MJ, Mohan D. Postural sway in dual-task conditions between spastic diplegic cerebral palsy and typically developing children. International Journal of Health and Rehabilitation Sciences. 2013; 2(2):91-7.
- Grecco LA, Tomita SM, Christovão TC, Pasini H, Sampaio LM, Oliveira CS. Effect of treadmill gait training on static and functional balance in children with cerebral palsy: a randomized controlled trial. Brazilian journal of physical therapy. 2013; 17(1):17-23. [DOI:10.1590/S1413-35552012005000066]
- Sharif-Moradi K, Farah-Pour N. [Comparison of the balance performance of the children with spastic cerebral palsy before and after exercise therapy program (Persian)]. Archives of Rehabilitation. 2006; 7(1):22-8.
- Ebrahimi Etri A, Asghari L. Comparison of two exercise methods on motor performance and balance in children with spastic cerebral palsy. Journal of Rehabilitation. 2012; 13(1):79-87.
- Ismailiyan M, Marandi S, Ghardashi Afousi A, Movahedi A, Esfarjany F. Effect of progressive resistance and balance training on upper trunk muscle strength of children with cerebral palsy: A case study. Journal of Rehabilitation. 2016; 17(1):84-93. [DOI:10.20286/jrehab-170182]
- Mutlu A, Livanelioglu A, Gunel MK. Reliability of Ashworth and modified Ashworth scales in children with spastic cerebral palsy. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2008; 9(1):44. [DOI:10.1186/1471-2474-9-44] [PMID] [PMCID]
- Colver A. Study protocol: SPARCLE: A multi-centre European study of the relationship of environment to participation and quality of life in children with cerebral palsy. BMC Public Health. 2006; 6(1):105. [DOI:10.1186/1471-2458-6-105] [PMID] [PMCID]
- Pavão SL, dos Santos AN, Woollacott MH, Rocha NACF. Assessment of postural control in children with cerebral palsy: A review. Research in Developmental Disabilities. 2013; 34(5):1367-75. [DOI:10.1016/j.ridd.2013.01.034] [PMID] [PMCID]
- Riley PO, Benda BJ, Gill-Body KM, Krebs DE. Phase plane analysis of stability in quiet standing. Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development. 1995; 32(3):227-35. [PMID]
- Hatzitaki V, Zlsi V, Kollias I, Kioumourtzoglou E. Perceptual-motor contributions to static and dynamic balance control in children. Journal of Motor Behavior. 2002; 34(2):161-70. [DOI:10.1080/00222890209601938] [PMID]
- Teasdale N, Simoneau M. Attentional demands for postural control: the effects of aging and sensory reintegration. Gait & Posture. 2001; 14(3):203-10. [DOI:10.1016/S0966-6362(01)00134-5]
- Deviterne D, Gauchard GC, Jamet M, Vançon G, Perrin PP. Added cognitive load through rotary auditory stimulation can improve the quality of postural control in the elderly. Brain Research Bulletin. 2005; 64(6):487-92. [DOI:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2004.10.007] [PMID]
- Kim SJ, Kwak EE, Park ES, Cho SR. Differential effects of rhythmic auditory stimulation and neurodevelopmental treatment/ bobath on gait patterns in adults with cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation. 2012; 26(10):904-14. [DOI:10.1177/0269215511434648] [PMID]
فهرست منابع
1. Rosenbaum P, Paneth N, Leviton A, Goldstein M, Bax M, Damiano D, et al. A report: The definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology. 2007; 109:8-14. [PMID]
2. Odding E, Roebroeck ME, Stam HJ. The epidemiology of cerebral palsy: Incidence, impairments and risk factors. Journal Disability and Rehabilitation. 2006; 28(4):183-91. [DOI:10.1080/09638280500158422 ] [PMID] [DOI:10.1080/09638280500158422]
3. Case-Smith J, O'Brien JC. Occupational therapy for children and adolescents. New York: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2014.
4. Soleimani F, Vameghi R, Rassafiani M, Akbar Fahimi N, Nobakht Z. Cerebral palsy: Motor types, gross motor function and associated disorders. Iranian Rehabilitation Journal. 2011; 9:21-31.
5. Akbar Fahimi N, Hosseini SA, Rassafiani M, Farzad M, Haghgoo HA. The reactive postural control in spastic cerebral palsy children. Iranian Rehabilitation Journal. 2012; 10(1):66-74.
6. Melzer I, Damry E, Landau A, Yagev R. The influence of an auditory–memory attention-demanding task on postural control in blind persons. Clinical Biomechanics. 2011; 26(4):358-62. [DOI:10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2010.11.008] [PMID] [DOI:10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2010.11.008]
7. Shumway-Cook A, Woollacott MH. Motor control: Translating research into clinical practice. Philadephia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007.
8. Maurer C, Mergner T, Bolha B, Hlavacka F. Vestibular, visual, and somatosensory contributions to human control of upright stance. Neuroscience Letters. 2000; 281(2-3):99-102. [DOI:10.1016/S0304-3940(00)00814-4] [DOI:10.1016/S0304-3940(00)00814-4]
9. Shumway-Cook A, Woollacott M. Attentional demands and postural control: The effect of sensorycontext. Journals of Gerontology-Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2000; 55(1):M10-16. [DOI:10.1093/gerona/55.1.M10] [DOI:10.1093/gerona/55.1.M10]
10. Magnusson M, Johansson K, Johansson BB. Sensory stimulation promotes normalization of postural control after stroke. Stroke. 1994; 25(6):1176-80. [DOI:10.1161/01.STR.25.6.1176] [PMID] [DOI:10.1161/01.STR.25.6.1176]
11. Kwak EE. Effect of rhythmic auditory stimulation on gait performance in children with spastic cerebral palsy. Journal of Music Therapy. 2007; 44(3):198-216. [DOI:10.1093/jmt/44.3.198] [PMID] [DOI:10.1093/jmt/44.3.198]
12. Nobahar Ahari M, Nejati V, Hosseini SA. Attentional Demands of balance under Dual Task conditions in young adults. Iranian Rehabilitation Journal. 2012; 10(16):66-71.
13. Melzer I, Benjuya N, Kaplanski J. Age-related changes of postural control: Effect of cognitive tasks. Gerontology. 2001; 47(4):189-94. [DOI:10.1159/000052797] [PMID] [DOI:10.1159/000052797]
14. Shumway-Cook A, Hutchinson S, Kartin D, Price R, Woollacott M. Effect of balance training on recovery of stability in children with cerebral palsy. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology. 2003; 45(9):591-602. [DOI:10.1017/S0012162203001099] [PMID] [DOI:10.1017/S0012162203001099]
15. Novak I, Mcintyre S, Morgan C, Campbell L, Dark L, Morton N, et al. A systematic review of interventions for children with cerebral palsy: State of the evidence. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology. 2013; 55(10):885-910. [DOI:10.1111/dmcn.12246] [PMID] [DOI:10.1111/dmcn.12246]
16. Champagne D, Corriveau H, Dugas C. Effect of hippotherapy on motor proficiency and function in children with cerebral palsy who walk. Physical & Occupational Therapy in Pediatrics. 2017; 37(1):51-63. [DOI:10.3109/01942638.2015.1129386] [PMID] [DOI:10.3109/01942638.2015.1129386]
17. Deutz U, Heussen N, Weigt-Usinger K, Leiz S, Raabe C, Polster T, et al. Impact of hippotherapy on gross motor function and quality of life in children with bilateral cerebral palsy: A randomized open-label crossover study. Thieme E-Books & E-Journals-Neuropediatrics. 2018; 49(3):185-92. [DOI:10.1055/s-0038-1635121] [PMID] [DOI:10.1055/s-0038-1635121]
18. Gorter JW, Currie SJ. Aquatic exercise programs for children and adolescents with Cerebral Palsy: What do we know and where do we go. International Journal of Pediatrics. 2011; 2011: 712165. [DOI: 10.1155/2011/712165] [PMID] [PMCID] [DOI:10.1155/2011/712165]
19. Reilly DS, Woollacott MH, van Donkelaar P, Saavedra S. The interaction between executive attention and postural control in dual-task conditions: children with cerebral palsy. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2008; 89(5):834-42. [DOI:10.1016/j.apmr.2007.10.023] [PMID] [DOI:10.1016/j.apmr.2007.10.023]
20. Samuel A, Solomon MJ, Mohan D. Postural sway in dual-task conditions between spastic diplegic cerebral palsy and typically developing children. International Journal of Health and Rehabilitation Sciences. 2013; 2(2):91-7.
21. Grecco LA, Tomita SM, Christovão TC, Pasini H, Sampaio LM, Oliveira CS. Effect of treadmill gait training on static and functional balance in children with cerebral palsy: a randomized controlled trial. Brazilian journal of physical therapy. 2013; 17(1):17-23. [DOI:10.1590/S1413-35552012005000066] [DOI:10.1590/S1413-35552012005000066]
22. Sharif-Moradi K, Farah-Pour N. [Comparison of the balance performance of the children with spastic cerebral palsy before and after exercise therapy program (Persian)]. Archives of Rehabilitation. 2006; 7(1):22-8.
23. Ebrahimi Etri A, Asghari L. Comparison of two exercise methods on motor performance and balance in children with spastic cerebral palsy. Journal of Rehabilitation. 2012; 13(1):79-87.
24. Ismailiyan M, Marandi S, Ghardashi Afousi A, Movahedi A, Esfarjany F. Effect of progressive resistance and balance training on upper trunk muscle strength of children with cerebral palsy: A case study. Journal of Rehabilitation. 2016; 17(1):84-93. [DOI:10.20286/jrehab-170182] [DOI:10.20286/jrehab-170182]
25. Mutlu A, Livanelioglu A, Gunel MK. Reliability of Ashworth and modified Ashworth scales in children with spastic cerebral palsy. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2008; 9(1):44. [DOI:10.1186/1471-2474-9-44] [PMID] [PMCID] [DOI:10.1186/1471-2474-9-44]
26. Colver A. Study protocol: SPARCLE: A multi-centre European study of the relationship of environment to participation and quality of life in children with cerebral palsy. BMC Public Health. 2006; 6(1):105. [DOI:10.1186/1471-2458-6-105] [PMID] [PMCID] [DOI:10.1186/1471-2458-6-105]
27. Pavão SL, dos Santos AN, Woollacott MH, Rocha NACF. Assessment of postural control in children with cerebral palsy: A review. Research in Developmental Disabilities. 2013; 34(5):1367-75. [DOI:10.1016/j.ridd.2013.01.034] [PMID] [PMCID] [DOI:10.1016/j.ridd.2013.01.034]
28. Riley PO, Benda BJ, Gill-Body KM, Krebs DE. Phase plane analysis of stability in quiet standing. Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development. 1995; 32(3):227-35. [PMID]
29. Hatzitaki V, Zlsi V, Kollias I, Kioumourtzoglou E. Perceptual-motor contributions to static and dynamic balance control in children. Journal of Motor Behavior. 2002; 34(2):161-70. [DOI:10.1080/00222890209601938] [PMID] [DOI:10.1080/00222890209601938]
30. Teasdale N, Simoneau M. Attentional demands for postural control: the effects of aging and sensory reintegration. Gait & Posture. 2001; 14(3):203-10. [DOI:10.1016/S0966-6362(01)00134-5] [DOI:10.1016/S0966-6362(01)00134-5]
31. Deviterne D, Gauchard GC, Jamet M, Vançon G, Perrin PP. Added cognitive load through rotary auditory stimulation can improve the quality of postural control in the elderly. Brain Research Bulletin. 2005; 64(6):487-92. [DOI:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2004.10.007] [PMID] [DOI:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2004.10.007]
32. Kim SJ, Kwak EE, Park ES, Cho SR. Differential effects of rhythmic auditory stimulation and neurodevelopmental treatment/ bobath on gait patterns in adults with cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation. 2012; 26(10):904-14. [DOI:10.1177/0269215511434648] [PMID] [DOI:10.1177/0269215511434648]
ارسال پیام به نویسنده مسئول
| بازنشر اطلاعات | |
 |
این مقاله تحت شرایط Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License قابل بازنشر است. |